Mercury analysis is an essential process used by laboratories to detect and quantify mercury concentrations in various samples, such as environmental, food, and industrial applications. Accurate and precise results from mercury analysis are necessary for compliance with regulations, protecting public health, maintaining environmental safety, and, more importantly, making an informed decision in policy making.
Lab analysts sometimes face difficulties in achieving consistent outcomes. This article examines five reasons precision may be lacking when performing mercury analysis, along with suggestions on how to address them.
Reason 1: Errors Occurred During Wet Chemical Sample Preparation
The Wet Chemical Sample Preparation process involves wet oxidation and reduction, which converts all types of mercury into ionic mercury (Hg2+), and then reduces it to elemental mercury vapor (Hg0). However, this multi-step process is highly susceptible to errors and inconsistencies.
The process requires various acids, oxidizing agents, and reducing agents before the final measurement can be taken. This makes it vulnerable to inaccuracies caused by reagents, glassware cleanliness, the water source used for chemical preparation, and last but not least, human handling to perform all the tasks. As a result, the process is susceptible to these factors, and any errors can significantly impact the overall accuracy and reliability of the results.
Common errors in this process include contamination, incomplete digestion, and sample loss during preparation. To improve sample preparation:
- Follow established protocols for collecting, storing, and handling samples
- Utilize a clean and dedicated set of glassware for mercury analysis
- Use reagent with high purity grade (that has low mercury background)
- Monitor digestion procedures to guarantee complete sample dissolution
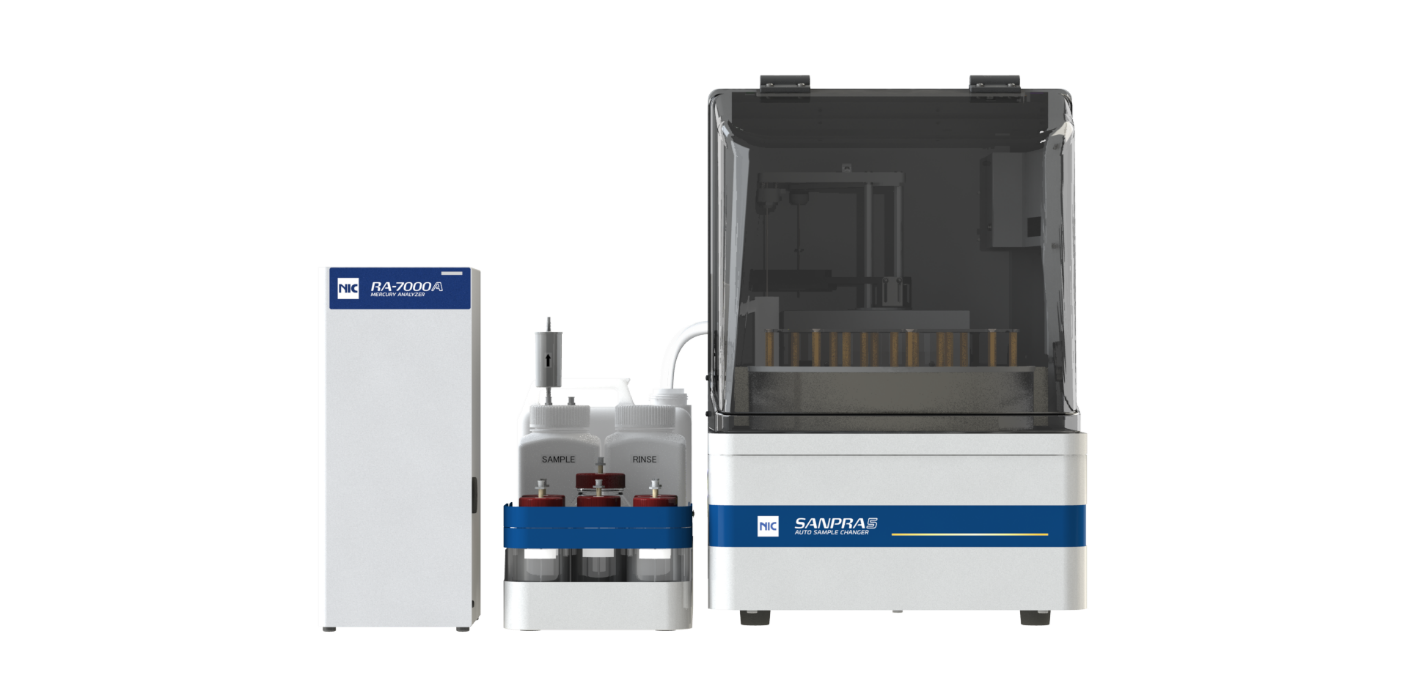
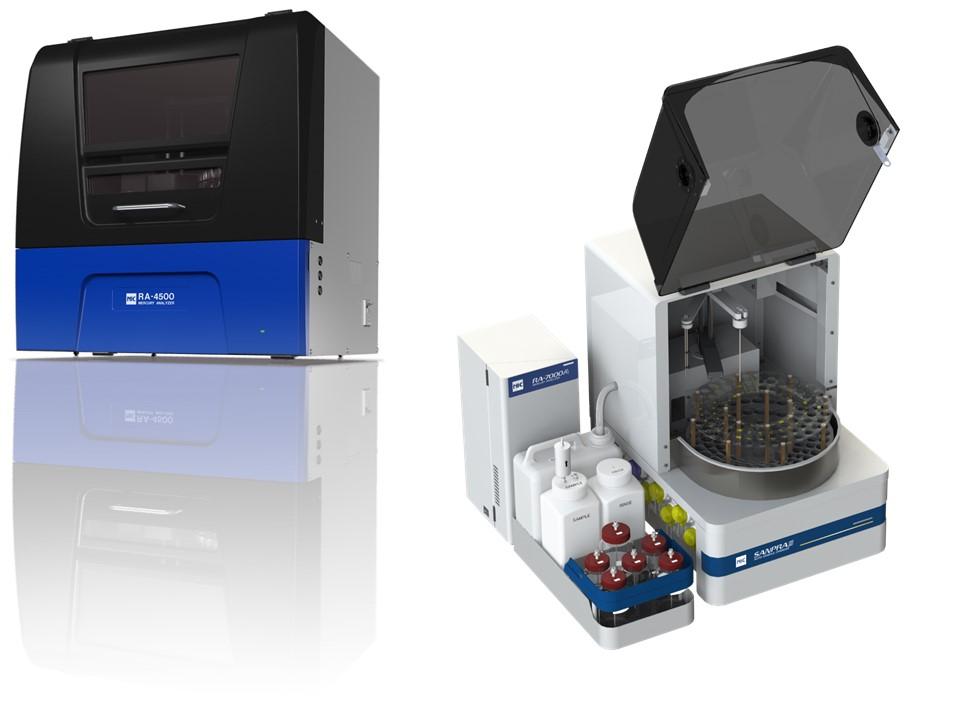
- Utilize mercury analyzer with a higher degree of automation
Reason 2: Instrument Calibration or Maintenance Issues
Proactive Instrument calibration and maintenance are crucial for optimum, efficient laboratory operation. Likewise, regular preventive maintenance on the mercury analyzer is necessary to ensure precise and accurate mercury analysis.
Calibration errors can arise due to drift over time or incorrect calibration standards, so lab analysts must ensure that both are done accurately. They can ensure proper calibration and upkeep by:
- Regular calibration of instruments using appropriate standards
- Standards are properly prepared and stabilized
- Regular maintenance of water source
- Documenting calibration procedures and results
- Implementing a proactive maintenance schedule with a mercury analyzer supplier or manufacturer for the analyzer.
Reason 3: Variability in Analysis Methods
When selecting an analytical technique for mercury analysis, there are multiple techniques available, each with its own detection limits, sensitivity levels, and potential matrix interferences. Variability between these methods can significantly impact accuracy and precision. In order to select the most suitable one for a specific application, lab analysts should:
- Evaluate the advantages and drawbacks of various mercury analysis techniques
- Refer to relevant regulations and guidelines for method selection
- Collaborate with experienced colleagues or industry experts to select the most effective approach
Reason 4: Analyst Training & Expertise
Human factors play a vital role in mercury analysis accuracy and precision. Common analyst errors include inconsistent wet chemical sample preparation handling and misinterpreting instrument readings. To reduce these issues, laboratories can consider investing in comprehensive training, and ongoing professional development for their analysts and utilizing mercury analyzer that offers a higher degree of automation. This includes:
- Get regular updates from mercury analyzer manufacturers on best practices and new technologies in mercury analysis
- Fostering collaboration and knowledge-sharing among lab staff and other agencies that also perform mercury analysis
- Actively participate in special cooperative efforts for joint monitoring programs such as APMMN that specializes in rainwater monitoring across the Asia-Pacific region
- Offering opportunities for professional growth and development within the field of mercury analysis, such as participating in the bi-annual International Conference on Mercury as a Global Pollutant (ICMGP) to gather the latest development, demands and challenges in mercury analysis
Reason 5: Environmental and Laboratory Conditions
Temperature, humidity, and pressure can significantly impact mercury analysis results too. Furthermore, contaminants from the laboratory environment may also skew results, causing false positives in the measurement. Mercury concentration normally occurs in the trace and ultra-trace levels. To maintain good laboratory conditions to perform analysis on such concentrations level, analysts should:
- Monitor and maintain clean environmental conditions in the lab by implementing strict cleanliness protocols
- Use appropriate fume hoods, filters, and enclosures to avoid cross-contamination.
- Perform regular maintenance checks on fumehood
- Mercury analyzer reagents should be kept in dedicated storage to avoid cross-contamination from the external environment
Laboratory analysts can enhance the accuracy and dependability of their results by addressing the top five potential causes of imprecise mercury analysis. In turn, this ensures that regulatory requirements are met and that public health and the environment are protected, facilitating informed decision-making and policy formulation regarding mercury emissions.