Introduction:
The analysis of mercury in water is vital, as it profoundly influences the safety of both food and water sources. There’s a direct relationship: higher mercury levels in aquatic environments lead to increased mercury content in seafood due to bioaccumulation. This necessitates the continuous monitoring of mercury, highlighting its importance not only for environmental integrity but also for public health, particularly in communities dependent on seafood. Methylmercury, a highly toxic form of mercury, presents significant risks to marine life and humans consuming affected fish. This underscores the need for vigilant oversight to pinpoint and reduce mercury pollution sources. This ensures the preservation of healthy ecosystems and the well-being of dependent populations. Moreover, meeting regulatory guidelines designed to curtail mercury emissions relies on accurate and regular assessments. Such diligent analysis is essential to the global initiative addressing this pervasive environmental challenge, paving the way for a more sustainable future.
Mercury continues to haunt the present generation
The relentless endeavors of the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) have significantly enhanced global awareness of mercury’s dangers since the devastating Minamata tragedy. This catastrophic event, which marked the first recorded death due to mercury poisoning in 1956, highlighted the insidious nature of this pollutant.
Mercury, a silent and colorless contaminant, has claimed countless innocent lives over the years. It particularly affects communities for whom seafood is not merely a dietary preference but a staple. Although the awareness of mercury poisoning has improved over time, this pollutant continues to lurk around areas with extreme poverty where Artisanal Small Scale and Gold Mining is the activity to make ends meet.
Certain groups use elemental mercury to “clean” or extract the ore, resulting in the water used from washing in the process leaking to nearby terrain and ecosystems. Thus, water mercury analysis is far from a luxury but a necessity to ensure that we do not repeat Minamata tragedy.
Existing Method of Mercury Analysis in Water Sample
Mercury analysis is often performed on various types of water samples, such as groundwater, surface water and wastewater. Each type has varying levels and sources of mercury contamination which makes accurate measurement necessary.
Several regulatory methods, such as EPA, APHA, ASTM, and JIS, have similar methods of water mercury analysis. Traditionally, water mercury analysis is time-consuming and extremely labor-intensive. From the sample preparation, the water sample must be digested for 2 hours with multiple hazardous reagents such as concentrated sulfuric acid, concentrated nitric acid, potassium permanganate, potassium persulfate, hydroxylamine hydrochloride and followed by Tin (II) Chloride.
Performing these steps manually could introduce potential errors in the measurement results. Moreover, the methods typically involve concentrated acids and potent oxidants, posing significant safety hazards to those handling these hazardous substances, underscoring the need for the adoption of automated systems to minimize human error and work hazard exposure.
Following most regulatory methods for mercury measurement also requires clean glassware to avoid pseudo-positives or biased results.
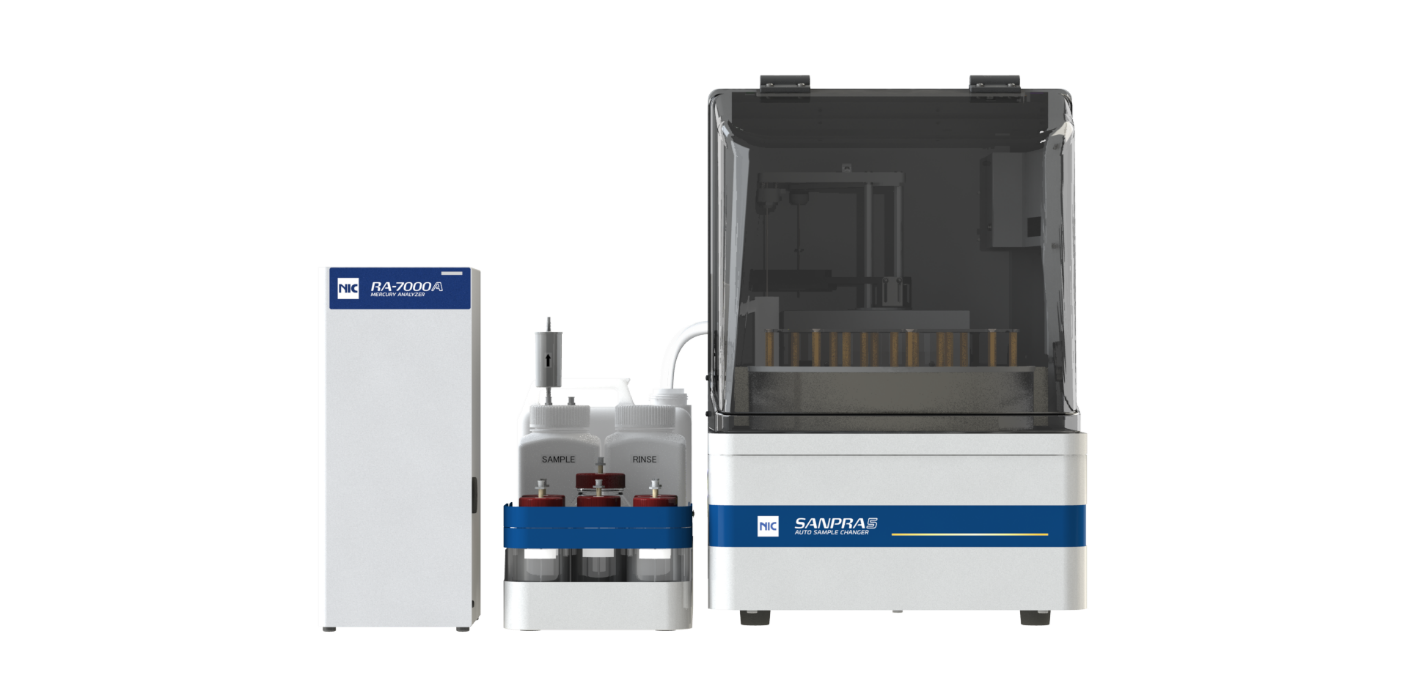
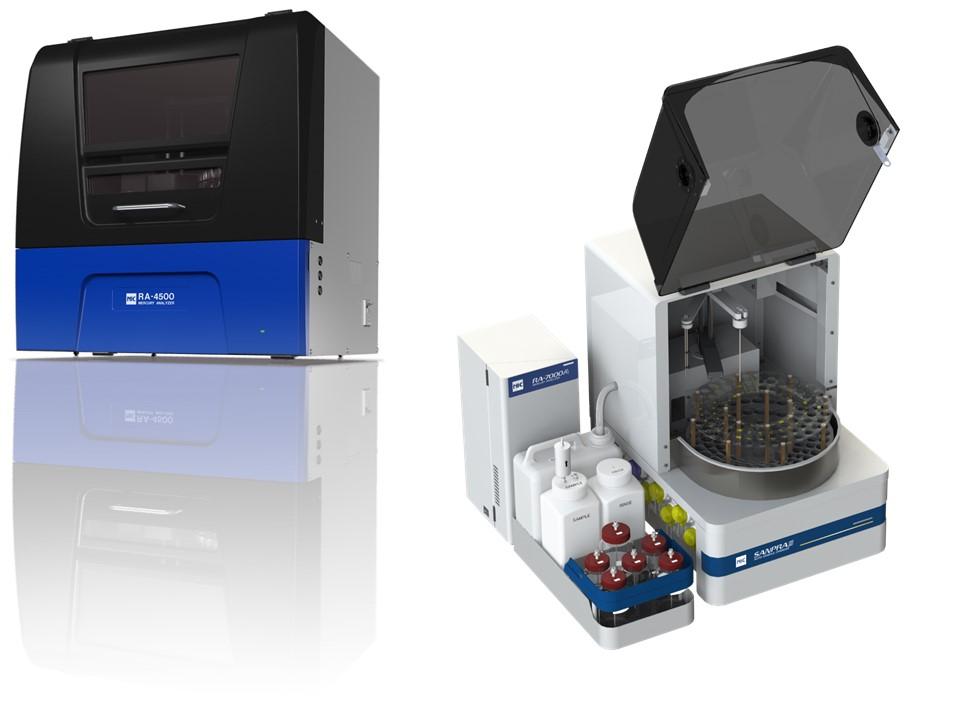
How NIC RA-7000A Accurately Measures Water Sample:

Nippon Instruments Corporation’s RA-7000A offers an innovative solution to overcome the difficulties encountered with traditional mercury analysis methods by utilizing an Automated Discrete-Direct-Purge (DDP) Reducing Vaporization technique.
Automation
The RA-7000A fully automates all steps from sample digestion to measurement. It is the only CVAAS in the market that automates the entire process with full method compliance such as EPA 245.1, APHA 3112B, ASTM and JIS K0102.
It automates the steps of dispensing concentrated sulfuric acid, concentrated nitric acid, potassium permanganate, potassium persulfate, hydroxylamine hydrochloride and Tin (II) Chloride. All users have to do is to dispense 5mL of water sample into each sample tube, fill up reagent bottle, select the right method and press START. RA-7000A together with SANPRA™ 5 will perform the sample chemical digestion for you with the right sequence of reagents and at the required temperature.
Discrete-Direct-Purge (DDP) Reducing Vaporization Technique
In DDP technique, all chemical reactions happened in each sample tube respectively. Instead of pumping up the sample solution flowing through a sample tubing to slowly mix it up with necessary chemicals, in DDP technique, all reagents are dispensed directly into the sample tube according to method sequence.

Upon reaction completion, the reducing agent Tin (II) Chloride, SnCl2, converts all mercury forms into elemental mercury. From here, elemental mercury which is insoluble in aqueous will be purged out from the sample solution by a stream of clean air and transported into the CVAAS detector for measurement. Throughout the entire pathway, it is dry and inert and thus, eliminating sample-to-sample carryover or mercury memory effect.
Therefore, the DDP technique prevents ionic mercury from adhering to surfaces. Only elemental mercury will be transported along the pathway. Hence, the user can eliminate sample-to-sample carryover or the memory effect. This technique produces highly precise and dependable results with reduced hazardous mercury waste production to less than one liter per day of operation.

Conclusion:
Accurate and reliable method of mercury analysis in water samples is critical for protecting public health and the environment. Nippon Instruments Corporation’s RA-7000A offers a unique and highly effective solution to overcome traditional mercury analysis methods.
The Discrete-Direct-Purge Reducing Vaporization technique truly eliminates sample-to-sample carryover or memory effect, producing highly precise results with little room for error. With high sensitivity, precision, and speed – making RA-7000A an ideal choice for water mercury analysis.
Check out Application Notes for RA-7000A