Resources
Certified Reference Material (CRM) for Mercury

National Institute for Minamata Disease (NIMD)
The National Institute for Minamata Disease (NIMD) is supplying the complimentary CRM to facilitate a global understanding and management of mercury pollution. As a leading research institution specializing in Minamata disease and mercury, NIMD is committed to sharing its extensive knowledge and expertise to address mercury pollution issues worldwide.
History of NIMD
NIMD was founded in 1978 in Minamata City, Kumamoto, to advance research and medical care for Minamata disease patients. It is part of Ministry of Environment, Japan.
Reorganized in 1996, it expanded its research functions and established the Department of International Affairs and Research. In 2001, NIMD opened the Minamata Disease Archives. Integrated into the National Environmental Research and Training Institute in 2003, NIMD enhanced its research capabilities. Following the adoption of the Minamata Convention on Mercury in 2013, NIMD focuses on disseminating research outcomes and mercury management technologies globally.
WHO Collaborating Centre
Recognized as a WHO Collaborating Centre, NIMD collaborates with international organizations to develop and implement effective strategies for mercury pollution control, thereby contributing to global environmental health and safety.
By providing complimentary CRM, NIMD aims to support researchers, policymakers, and practitioners in their efforts to monitor and mitigate mercury pollution, ensuring a healthier and safer environment for all.
Certified Reference Material (CRM)
Certified Reference Material (CRM) or Standard Reference Material are always needed by analysts to confirm the performance of the instrument and to ensure that sample measurement result is accurate.
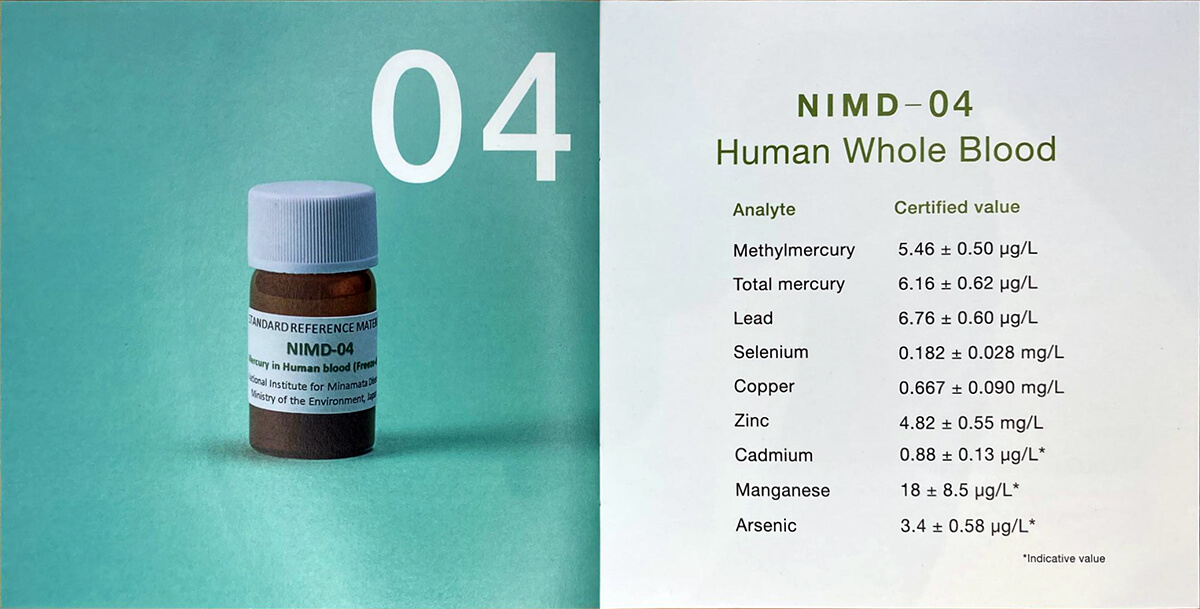
Whole blood, urine and hair are some of the best matrices to assess mercury’s impact on local human health. For instance, studying the mercury content at different parts of the hair will indicate the timeline of mercury exposure of that individual.

Certified Reference Material (CRM)
Certified Reference Material (CRM) or Standard Reference Material are always needed by analysts to confirm the performance of the instrument and to ensure that sample measurement result is accurate.
Whole blood, urine and hair are some of the best matrices to assess mercury’s impact on local human health. For instance, studying the mercury content at different parts of the hair will indicate the timeline of mercury exposure of that individual.
However, commercially available biological samples of CRM for mercury analysis is hard to get by.
With the increasing demand of the need of measuring mercury in mercury impact assessment towards human, National Institute for Minamata Disease (NIMD) under the Ministry of Environment Japan has developed a series of biological CRM such as whole blood, urine and hair.

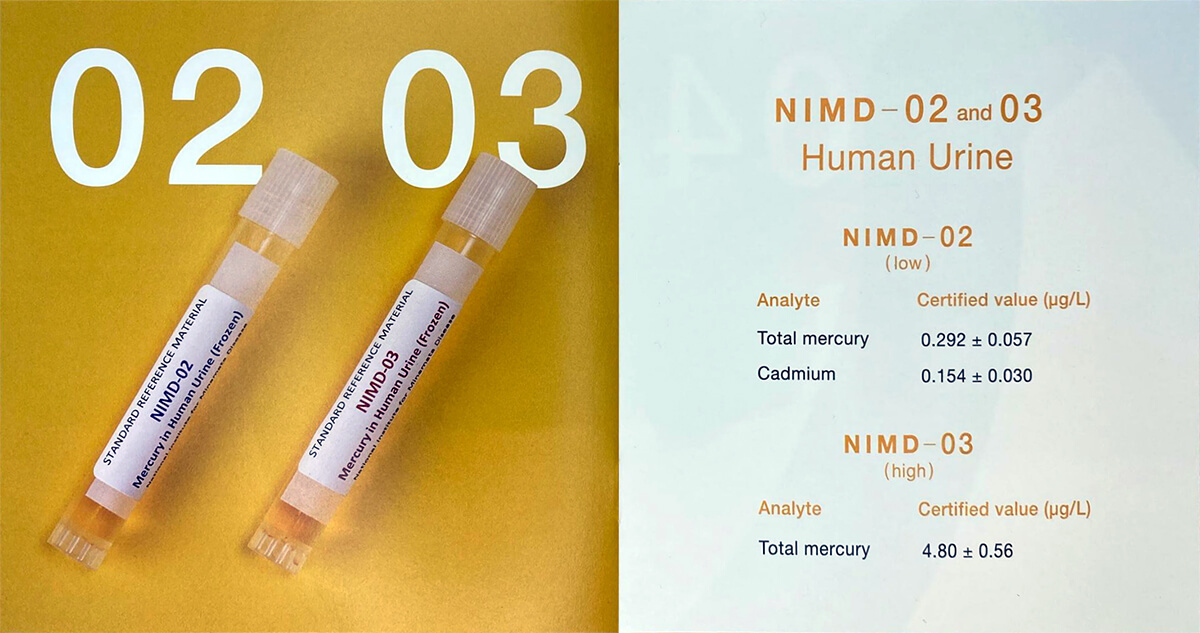
In accordance with ISO Guide 35 (JIS Q 0035), NIMD has developed Certified Reference Materials (CRMs) for hair, urine, and blood. These CRMs are designed to validate the accuracy of analytical methods and equipment, as well as to manage precision in the quantitative analysis of trace elements. The products are registered with RMinfo (Reference Materials Total Information Services of Japan) and listed in the COMAR Certified Reference Materials database, making them easily searchable and accessible for reference.

Cost of NIMD Certified Reference Materials
All CRMs are provided Free of Charge (FOC) for eligible recipients.
Distribution Destinations and Conditions
The CRMs are available for distribution to national and public research institutions (including Incorporated Administrative Agencies), organizations conducting research and surveys related to the implementation of the Minamata Convention on Mercury, and research laboratories at educational institutions such as universities. Although the CRMs are provided free of charge, NIMD requests that recipients answer the following questions at the time of request. Generally, the transfer or sale of distributed CRMs is prohibited.
Since CRMs serve as a golden standard of confirmation, its preparation laboratory must be certified and traceable. The National Institute for Minamata Disease has been accredited as a laboratory based on JIS Q 17025:2018 (ISO/IEC 17025:2017) with flexible scope.

Contact for NIMD’s Certified Reference Material (CRM)
For parties that are interested in the CRMs, please visit nimd.env.go.jp for more information.
If you wish to request distribution, please send us an e-mail, specifying the following pieces of information, at: [email protected]
(Person in charge: Koichi Haraguchi, Mercury Analysis Technique Section)
(Person in charge: Koichi Haraguchi, Mercury Analysis Technique Section)

